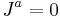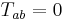Vacuum solution
A vacuum solution is a solution of a field equation in which the sources of the field are taken to be identically zero. That is, such field equations are written without matter interaction (i.e.- set to zero).
Contents |
Examples
- In Maxwell's theory of electromagnetism, a vacuum solution would represent the electromagnetic field in a region of space where there are no electromagnetic sources (charges and electric currents), i.e. where the current 4-vector vanishes:[1]
- Einstein's theory of general relativity where a vacuum solution[2] would represent the gravitational field in a region of spacetime where there are no gravitational sources (masses), i.e. where the energy-momentum tensor vanishes:[3]
- Kaluza-Klein vacuum (static) field equations[4]
- Kasner vacuum solution [5]
See also
- Maxwell's equations#In vacuum
- Kerr vacuum
- Einstein field equations
- Ernst vacuum
- Kasner metric
- Vacuum solution (general relativity)
References
- Gott, J.R.; Richard, J. (1985), "Gravitational lensing effects of vacuum strings- Exact solutions", Astrophysical Journal 288 (Part 1), Bibcode 1985ApJ...288..422G, doi:10.1086/162808
- Friedrich, H.; Nagy, G. (1999), "The initial boundary value problem for Einstein's vacuum field equation", Communications in Mathematical Physics 201 (3): 619–655, Bibcode 1999CMaPh.201..619F, doi:10.1007/s002200050571, http://math.msu.edu/~gnagy/papers/hFgN99.pdf, retrieved 2009-07-04
- Appelquist, T.; Chodos, A. (1983), "Quantum dynamics of Kaluza-Klein theories", Physical Review D 28 (4): 772–784, Bibcode 1983PhRvD..28..772A, doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.28.772
Notes
- ^ Esposito, S. (1997), "Classical vgr? c solutions of Maxwell's equations and the photon tunneling effect", Physics Letters A 225 (4-6): 203–209, arXiv:physics/9611018, Bibcode 1997PhLA..225..203E, doi:10.1016/S0375-9601(96)00872-9, http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0375960196008729, retrieved 2009-07-04
- ^ Stephani, H. (2003), Exact solutions of Einstein's field equations, http://www.loc.gov/catdir/samples/cam033/2002071495.pdf, retrieved 2009-07-04
- ^ Quevedo, H. (1990), "Multipole Moments in General Relativity-Static and Stationary Vacuum Solutions", Fortschritte der Physik/Progress of Physics 38 (10): 733, Bibcode 1990ForPh..38..733Q, doi:10.1002/prop.2190381002, http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/112587363/abstract, retrieved 2009-07-04
- ^ Sorkin, R.D. (1983), "Kaluza-klein monopole", Physical Review Letters 51 (2): 87–90, Bibcode 1983PhRvL..51...87S, doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.51.87
- ^ Chodos, A.; Detweiler, S. (1980), "Where has the fifth dimension gone?", Physical Review D 21 (8): 2167–2170, Bibcode 1980PhRvD..21.2167C, doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.21.2167